Relay is another interesting electronic component, lets see how it looks ...


This big black box, is this a relay ?... but what is this for ??
These type of questions are obvious to jumbling in your mind, but you will really appreciate this device and its importance once you understand its working and functionality.
Basically, relays are used as switches. These are different from those manual switches where we push button to turn them on and off. Relays are electromagnetic device, and very useful in scenarios where we want to control a high voltage device through our small low-voltage circuit. So basically a relay is electrically operated switch.
For example, assume that you have designed a small water pump controller which works on 5V DC. And with this controller you need to control a water pump which works on 110v AC. Now the question is how will you control a 110V AC water pump with a 5v controller? The answer is very simple .. Use relay as show in the diagram below.
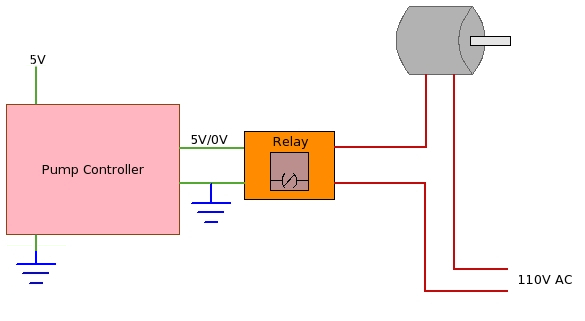
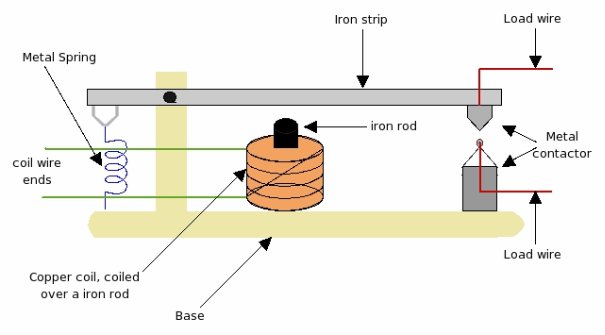
Now lets understand the principle of relay and how it works. Relay works on the principle of electromagnetism, look the diagram below
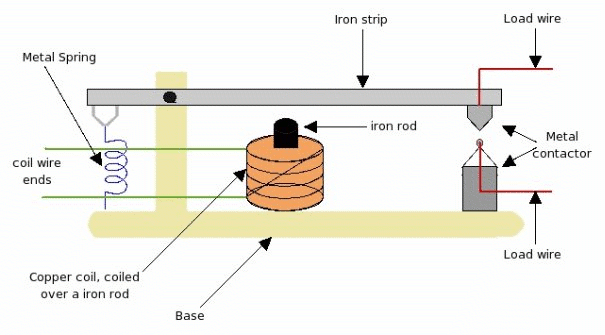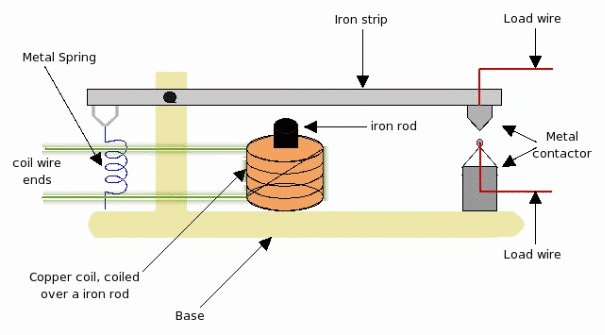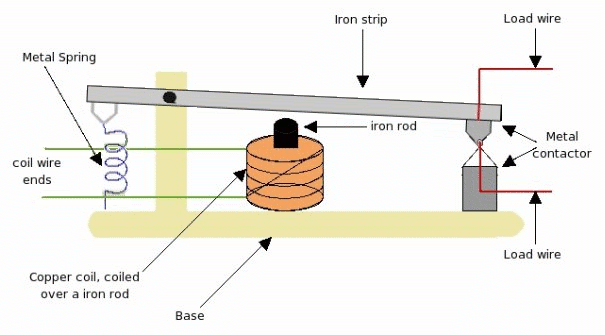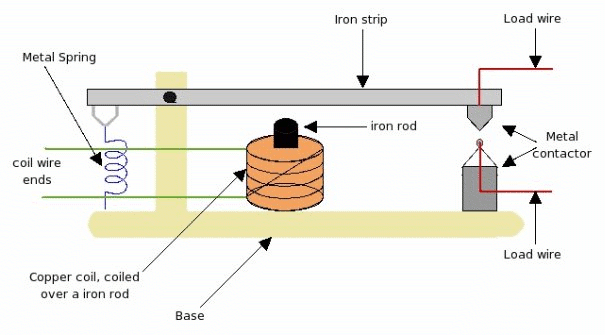
Working of relay is very simple. When small voltage of 5v is applied to the copper coil, since this coil is coiled over a iron rod, the iron rod gets magnetized. Due to this magnetism iron-rod attracts the iron-strip above it. As the iron strip is pivoted, the magnetic force pulls iron-strip pulled toward the iron-rod. Due to this pulling force, the metal connectors make contact, and the load wire connected to connector completes the load-line circuit. As long small voltage is supplied to the coil, magnetic strip will pulled, metallic-contractor will make contact, and load-line circuit will be ON. Please note that the magnetic pull force should be more than the spring force to pull the strip down and make the relay ON.
But, as 5V is changed to 0V, the coil will no longer be able to create the magnetic force and the iron-rod will get de-magnetized. As a result the iron-rod will not be able to pull the iron-strip down. Now the spring force will come into picture which will cause iron strip to move away from iron rod. As a result metallic connector will also get apart, and this will disconnect the load line circuit, turning load-line circuit to OFF .